html" title=爬虫>爬虫大致可以分为三步:
- 第一步,发送request请求获得html内容
- 第二步,清洗数据,即从html原网页数据中筛选我们需要的数据
- 第三步,将需要的数据储存
在第二步筛选数据是,我们往往可以利用BeautifulSoup来完成,下面就如何利用BeautifulSoup来解析原html网页数据并获取我们需要的内容进行讲解。
1 认识HMTL的结构 – 预备知识
html中有两个很重要的概念就是标签和属性,可以说html就是有一个一个的标签和标签之间的内容构成的,标签位于<>之后,通常都是成对出现。
详细内容参可以参考:菜鸟教程html
1.1 标签
标签位于<>之中,一般都是成对出现,格式如下:
<标签>内容</标签>
直接上上一段html代码,所有红色字体部分都是标签:
html"><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link0">link0</a -->
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p>一个图像:<img src="smiley.gif" alt="Smiley face" width="32" height="32"></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">this a new story</p>
</body>
</html>
代码中,所有红色字体的都是标签,比如、
,并且标签都是成对出现, 起始标签和结束标签之间的白色字体部分(可能嵌套了其他标签)就是文本内容。这段html的显示效果如下:

1.2 属性
属性,就是用来描述标签的一些特性,比如 < a>标签代表是链接,href属性就是给定了这个标签链接的具体地址。再比如,标签代表图像,src代表了图片的路径,width和height属性分别指定了图片的宽度和高度。属性位于起始所在的<>中,并且跟在起始标签的后面,格式如下:
<标签 属性名1= 属性值1 属性名2 = 属性值2>内容</标签>
上面html代码中,橘黄色部分就是属性名,绿色部分就是对应的属性值,中间用=连接
1.3 文本内容与标签内容
这两个概念可能并不准确,只是为了方便后续描述。因为使用BeautifulSoup方法时,返回的内容基本上都是标签内容或文本内容。
这简单来说,起始标签和结束标签之间的所有部分(包含起始标签和结束标签)就是这个标签对应的标签内容。而文本内容就是位于起始标签和结束标签之间、<>之外的的部分。这句话感觉有点奇怪,该怎么理解呢?
举个例子:
html"><title>The Dormouse's story</title>
对于title来说,标签内容是:<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
文本内容就是:The Dormouse's story
html"><p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
对于标签p来说,文本内容就是:The Dormouse’s story,因为中间嵌套了另外一个标签b,但是内容是不算b的,因为b属于标签,位于<>之中。当然也可以说标签b的文本内容是:The Dormouse’s story。这个标签的标签内容就是:<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
为上面要强调这个概念呢?因为html" title=爬虫>爬虫很多时候都是需要获取文本内容,BeautifulSoup很多方法返回的就是标签内容或标签内容组成的列表,标签内容进一步通过**.string或者.text就可以得到文本内容**。
2 初识BeautifuSoup
2.1 BeautifulSoup四大对象
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种:
- Tag, 标签,即对应html中的标签
- NavigableString,遍历字符串,即对应html中的内容
- BeautifulSoup,soup对象,可以看作是一个特殊的tag,代表文档的全部内容
- Comment,可以看作是特殊的NavigableString,代表文档中注释的字符串
由于BeautifulSoup将html文档转化成立包含四种对象的复杂树形结构,因此,可以利用着四种对象来获取html中不同的内容。
2.2 .tag获取一个标签内容
< 标签>起止标签以及这部分就是标签内容< /标签>, 很多时候我们需要先提取两个标签之间的那部分内容,为了方便叙述,成为标签内容。注意,这部分内容可能还嵌套了其它的标签。
假如我们已经构造了一个BeautifulSoup对象soup,那么就可以利用soup.tag的方式获取标签对应的那部分内容,注意这个内容是包含标签本身的。
废话少说,直接上html" title=python>python代码演示:
html" title=python>python">import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link0">link0</a -->
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p>一个图像:<img src="smiley.gif" alt="Smiley face" width="32" height="32"></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">this is a new story</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'xml')
print(soup.head)
print(soup.p)
print(soup.b)
显示结果如下:
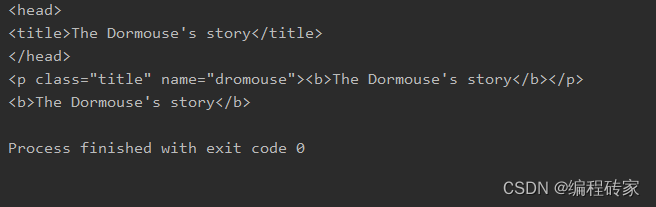
对比原来的html代码可以知道,soup.tag可以提取html中tag对应的那部分内容,并且保留了原来的格式。需要注意的是,如果html中有多个相同的标签,soup.tag只能提取里面的第一个标签对应的内容。
比如原html中有多个p标签,soup.p只是提取了第一个p标签代表的内容。如果要获取每个标签对应内容怎么办呢?可以使用find_all()函数,后面再讲。
从html代码我们可以知道,第一个p标签对应的内容如下:
html"><p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
我们还可以进一步提取里里面的属性值,方法如下:
soup.tag[属性名]:
html" title=python>python">print(soup.p['class'])
print(soup.p['name'])
上面两行代码显示如下:
title
dromouse
当然也可以用get函数来获取属性值:
soup.p.get(‘name’) 与 soup.p[‘name’] 效果是一样的。
另外需要说明的时,如果利用soup.tag获取某个标签内容,还可以对里面的标签内容进行遍历:
假如获取了某个个p标签内容如下:
html"><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
出去起始标签和结束标签之外,该p标签内容余下按部分按照嵌套的标签内容和文本内容可以分为7个部分:
html"><p class="story">【1 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were】
【2 <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>】【3 ,】
【4 <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>】 【5 and】
【6 <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>】【7 ;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.】
</p>
划分的依据就是,如果是新的标签或文本就是一个单独的元素。这样我们可以通过遍历的方式得到里面的每一个元素:
html" title=python>python"># 假如已经通过BeautifulSoup获取上面p标签内容tag_pContent,就可以遍历里面的7个元素了
for t in tag_pContent:
print(t)
2.3 .string或.text获取标签中间的文本内容
前面专门强调了文本内容这个概念,因为很多时候我们就是要获取标签之外的文本内容。
利用2.2中方法获取了标签内容之后,要获取文本内容就很简单了,因为文本内容包含在起始标签与结束标签之间。方法:
soup.tag.string或soup.tag.text, 其中,soup.tag获取了标签内容,再加上**.string或.text**就可以获取里面的文本内容了。
接着上面的例子:
print(soup.p.string) 或print(soup.p.text)就会显示如下:
The Dormouse’s story
2.4 BeautifulSoup可以看作是特殊的tag
BeautifulSoup 对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容.大部分时候,可以把它当作 Tag 对象,是一个特殊的 Tag,我们可以分别获取它的类型,名称,以及属性来感受一下:
html" title=python>python">print type(soup.name)
#<type 'unicode'>
print soup.name
# [document]
print soup.attrs
#{} 空字典
2.5 Comment
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其实输出的内容仍然不包括注释符号,但是如果不好好处理它,可能会对我们的文本处理造成意想不到的麻烦。
加入soup.a对应的内容如下:
html"><a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>
那么soup.a.string输出如下:
Elsie
实际上,Elsie是注释内容!,因此Comment可以看作是特殊的NavigableString对象。但是和类型不同,soup.a.string的类型为<class ‘bs4.element.Comment’>,因此为了造成意想不到的麻烦,可以用如下判断进行区分:
html" title=python>python">if type(soup.a.string)==bs4.element.Comment:
print("这是注释")
3 BeautifulSoup常用的一些函数或属性
find_all_184">3.1 find以及find_all函数返回标签内容
BeafutifulSoup中有很多函数,但是这个两个函数几乎是用得最多的,所以重点讲一下。find和find_all这两个函数和soup.tag获取的内容的形式都是一样,都是获取标签内容。
先看下函数原型吧:
html" title=python>python">find_all( tag_name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs ) # 返回列表
find( tag_name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs ) # 返回一找到的一个元素
这个两个函数区别就是,find只会返回满足条件的第一个标签内容,而find_all会将所有满足条件的标签内容以列表的形式返回。当find函数只使用第一个参数tag_name时,和soup.tag_name的效果时一样的。
比如:
soup.p和soup.find(‘p’)的结果是一样的。
比如对于下面这3个p标签,如何得到最后一个标签内容呢?可以利用标签属性进行过滤,第三个p标签具有class=’story‘的属性,但是前两个没有。
于时:
soup.find(‘p’, class_ =‘story’)
html"><p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p>一个图像:<img src="smiley.gif" alt="Smiley face" width="32" height="32"></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
html" title=python>python">print(soup.find('p'))
# 特别需要注意,由于class是html" title=python>python内置关键字,这里参数中需要用class_代替class
print(soup.find('p', class_='story'))
上面两行代码代码打印如下:
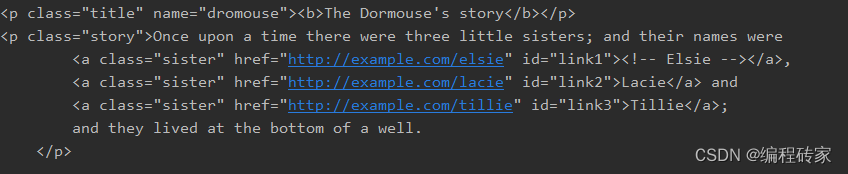
特别需要注意,由于class是html" title=python>python内置关键字,这里参数中需要用class_代替class
3.2 .strings 或.stripped_strings 属性获取所有的文本内容
.strings可以获取所有的文本内容组成的列表(需要通过遍历来访问),但是这个包含了一些原来文本中的一些空白字符,而.stripper_strings可以也是获取所有的文本内容,但是去掉了很多空格或空行。
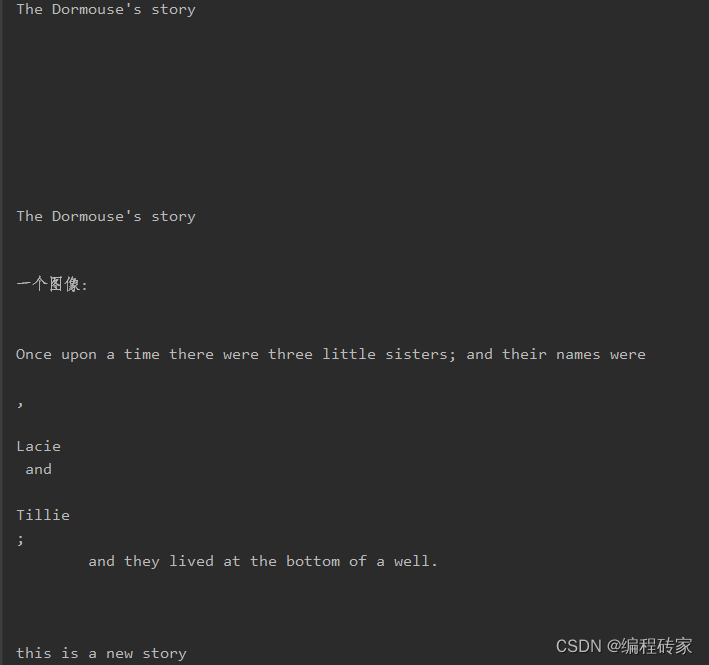
html" title=python>python">soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'xml')
for text in soup.strings: # 遍历所有的文本内容
print(text)
输出结果如下:
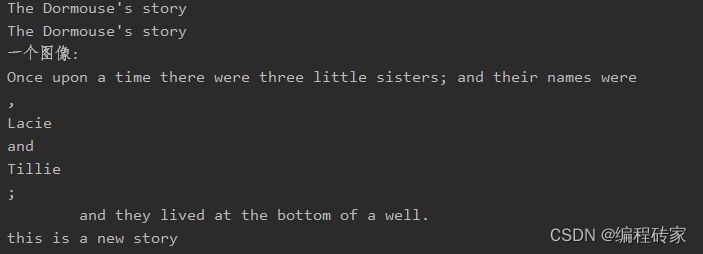
html" title=python>python">soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'xml')
for text in soup.stripped_strings: # 遍历所有的文本内容
print(text)
【参考文章】
1、Python中使用Beautiful Soup库的超详细教程